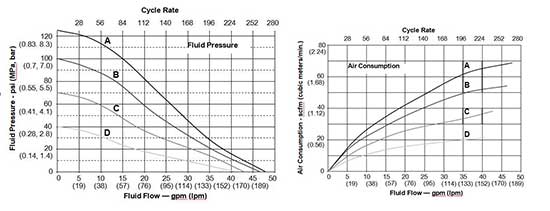
Graco Diaphragm Pump 1050PPP01AP2PPSPSPPT
Packing and shipping
|
Packaging Regulation : |
Wooden box |
|
Delivery time : |
7~14 days(About) |
|
Conditions : |
New and Genuine |

How do you order?
A&S makes ordering GET Parts easy. Simply send a mail to Us. Instead of searching online and guessing which parts you need, our team will make sure you get the correct parts. We process and deliver your order fast, and always at a competitive price. Enjoy 5-star service!
1.IDENTIFY
Determine the parts you need. To ensure the correct parts are quoted, it's best to have the machine make and model, along with part numbers and photos of the nameplate if possible. Our team of professionals are here to help ensure you get the correct parts that fit and work the first time. Our sales team can also survey and help identify the parts you may need. Please email us to get started!
2.ORDER
Our professional internal sales teams and strong supply chain system will assist you to identify the right parts, and can recommend the most cost-effective solution for you. Our team of professionals will process your order, and ensure your order is correct the first time. With over 15 years in the business, we remove the guesswork and always deliver.
3.DELIVER
We'll ship or deliver your products as required, to your nominated location. If you're also located elsewhere, we'll identify the best shipping options for both price and delivery time. Email us now!
1050PPP01AP2PPSPSPPT-A0215116
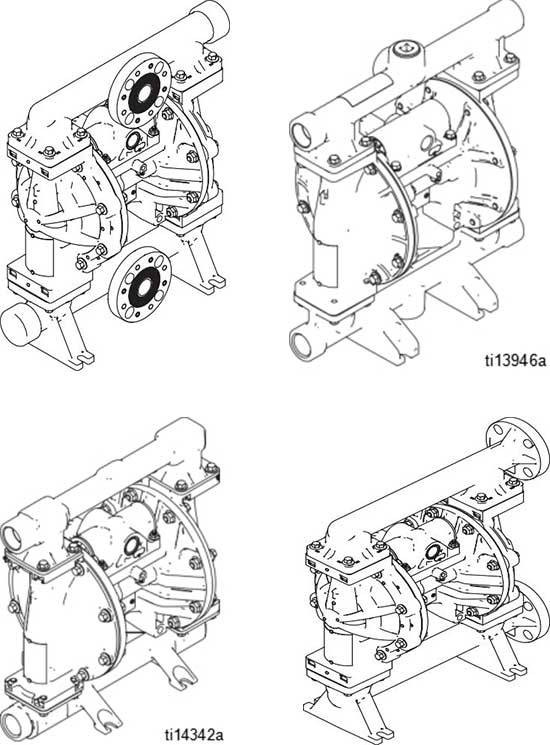
Husky 1050 Air-Operated Diaphragm Pump
1-inch pump with modular air valve for fluid transfer applications. For professional use only.
See page 4 for model information, including approvals.
125 psi (0.86 MPa, 8.6 bar) Maximum Fluid Working Pressure 125 psi (0.86 MPa, 8.6 bar) Maximum Air Input Pressure
Important Safety Instructions
Read all warnings and instructions in this manual. Save these instructions.
1050P Polypropylene 1050C Conductive
Polypropylene
1050F PVDF
Center Flange
Related Manuals
|
Manual |
Description |
|
313435 |
Husky 1050 Air-Operated Diaphragm Pump, Repair/Parts |
|
313597 |
Husky 1050A UL-Listed Diaphragm Pump, Operation |
|
313598 |
Husky 1050A CSA-Certified Diaphragm Pump, Operation |
|
313840 |
DataTrak, Instructions/Parts |
|
406824 |
Pulse Count Kits, Instructions |
To Find Your Nearest Distributor
1.Visit www.graco.com.
2.Click on Where to Buy and use the Distributor Locator.
To Specify the Configuration of a New Pump
Please call your distributor. OR
1.Use the Online Husky Selector Tool at wwwd.graco.com/training/husky/index.html.
2.If the link does not work, you will find the selector tool on the Process Equipment page at www.graco.com.
To Order Replacement Parts
Please call your distributor.
Distributor Note
1.To find part numbers for new pumps or kits, use the Online Husky Selector Tool.
2.To find part numbers for replacement parts:
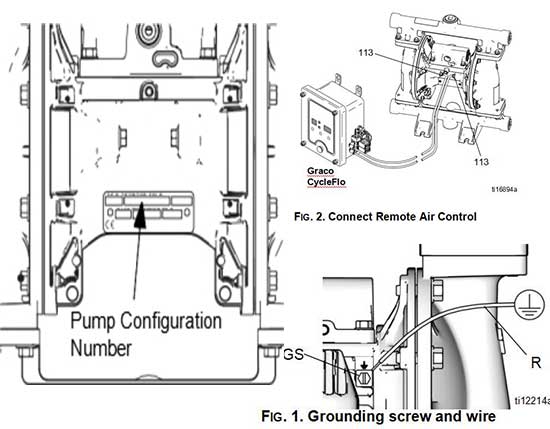
a.Use the configuration number from the ID plate on the pump. If you only have the Graco 6-digit part num- ber, use the selector tool to find the corresponding configuration number.
b.Use the Configuration Number Matrix on the next page to understand which parts are described by each digit.
c.Use the Repair/Parts Manual. Refer to the main Parts illustration and to the Parts/Kits Quick Reference. Follow the page references on these two pages for further ordering information, as needed.
3.Please call Graco Customer Service to order.
Configuration Number Matrix
Check the identification plate (ID) for the Configuration Number of your pump. Use the following matrix to define the components of your pump.
Sample Configuration Number: 1050A-PA01AA1SSBNBNPT
|
1050 |
A |
P |
A01A |
A1 |
SS |
BN |
BN |
PT |
|
Pump Size |
Wetted Section Material |
Drive Identifier |
Center Section and Air Valve |
Fluid Covers and Manifolds |
Seats |
Balls |
Diaphragms |
Manifold O-Rings |
|
Pump Size |
Wetted Section Material |
Drive Identifier |
Center Section and Air Valve Material |
Air Valve/Monitoring |
Fluid Covers and Manifolds |
|||
|
1050 |
A★◆ |
Aluminum |
P Pneumatic |
Aluminum |
A01A |
Standard |
A1 |
Aluminum, standard ports, inch |
|
1050 |
C★◆ |
Conductive Polypropylene |
A01B |
Pulse Count✖◆ |
A2 |
Aluminum, standard ports, metric |
||
|
|
A01C |
DataTrak✖ ◆ |
C1 |
Conductive polypropylene, center flange |
||||
|
1050 |
F |
PVDF |
A01D |
Remote |
||||
|
1050 |
H‡◆ |
Hastelloy |
A01E |
Optional FKM Seals |
C2 |
Conductive polypropylene, end flange |
||
|
1050 |
P |
Polypropylene |
AC1A |
CSA-Compliant |
||||
|
1050 |
S‡◆ |
Stainless Steel |
AU1A |
UL-Listed; Fuel transfer |
F1 |
PVDF, center flange |
||
|
|
AU3A |
UL-Listed; Fuel dispense✳ |
F2 |
PVDF, end flange |
||||
|
Conductive Polypropylene |
C01A |
Standard |
H1 |
Hastelloy, standard ports, inch |
||||
|
C01B |
Pulse Count✖ ◆ |
H2 |
Hastelloy, standard ports, metric |
|||||
|
C01C |
DataTrak✖ ◆ |
P1 |
Polypropylene, center flange |
|||||
|
C01D |
Remote |
P2 |
Polypropylene, end flange |
|||||
|
Polypropylene |
P01A |
Standard |
S1 |
Stainless steel, standard ports, inch |
||||
|
P01B |
Pulse Count✖ |
|||||||
|
P01C |
DataTrak✖ |
S2 |
Stainless steel, standard ports, metric |
|||||
|
P01D |
Remote |
|||||||
|
|
S5-1 |
Stainless steel, center flange, horizontal outlet port |
||||||
|
★, ‡, ◆, or ✖: See ATEX Certifications, page 4. ✳ Contains pressure relief valve. |
S5-2 |
Stainless steel, center flange, vertical outlet port |
||||||
|
Check Valve Seats |
Check Valve Balls |
Diaphragm |
Manifold O-Rings |
||||
|
AC |
Acetal |
AC |
Acetal |
BN |
Buna-N |
— |
Models with Buna-N, FKM Fluoroelastomer or TPE seats do not use o-rings. |
|
AL |
Aluminum |
BN |
Buna-N |
CO |
Polychloroprene Overmolded |
||
|
BN |
Buna-N |
CR |
Polychloroprene Standard |
FK |
FKM Fluoroelastomer |
||
|
FK |
FKM Fluoroelastomer |
CW |
Polychloroprene Weighted |
GE |
Geolast |
||
|
GE |
Geolast® |
FK |
FKM Fluoroelastomer |
PO |
PTFE/EPDM Overmolded |
||
|
PP |
Polypropylene |
GE |
Geolast |
PS |
PTFE/Santoprene Two-Piece |
PT |
PTFE |
|
PV |
PVDF |
PT |
PTFE |
PT |
PTFE/EPDM Two-Piece |
|
|
|
SP |
Santoprene® |
SP |
Santoprene |
SP |
Santoprene |
||
|
SS |
316 Stainless Steel |
SS |
316 Stainless Steel |
TP |
TPE |
||
|
TP |
TPE |
TP |
TPE |
|
|
||
All 1050A (Aluminum) and 1050C (Conductive Polypropylene) pumps are certified:
‡ 1050S (Stainless Steel) and 1050H (Hastelloy) pumps with aluminum or conductive polypropylene centers are certified:
◆
1050A (Aluminum) and 1050C (Conductive Polypropylene) pumps with DataTrak or Pulse Count AND 1050S (Stainless Steel) and 1050H (Hastelloy) pumps with aluminum or conductive polypropylene centers and fitted with DataTrak or Pulse Count are certified:
ATEX T-code rating is dependent on the temperature of the fluid being pumped. Fluid temperature is limited by the materials of the pump interior wetted parts. See Technical Specifications for the maximum fluid operating temperature for your specific pump model.
Warnings
The following warnings are for the setup, use, grounding, maintenance, and repair of this equipment. The exclama- tion point symbol alerts you to a general warning and the hazard symbol refers to procedure-specific risk. When these symbols appear in the body of this manual, refer back to these warnings. Additional, product-specific warnings may be found throughout the body of this manual where applicable.
WARNING
FIRE AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
Flammable fumes, such as solvent and paint fumes, in work area can ignite or explode. To help prevent fire and explosion:
•Use equipment only in well ventilated area.
•Eliminate all ignition sources; such as pilot lights, cigarettes, portable electric lamps, and plastic drop cloths (potential static arc).
•Keep work area free of debris, including solvent, rags and gasoline.
•Do not plug or unplug power cords, or turn power or light switches on or off when flammable fumes are present.
•Ground all equipment in the work area. See Grounding instructions.
•Use only grounded hoses.
•Hold gun firmly to side of grounded pail when triggering into pail.
•If there is static sparking or you feel a shock, stop operation immediately. Do not use equipment until you identify and correct the problem.
•Keep a working fire extinguisher in the work area.
Static charge may build up on plastic parts during cleaning and could discharge and ignite flammable materials and gases. To help prevent fire and explosion:
•Clean plastic parts in a well ventilated area.
•Do not clean with a dry cloth.
•Do not operate electrostatic guns in equipment work area.
SPECIAL CONDITIONS FOR SAFE USE
Equipment must comply with the following conditions to avoid a hazardous condition which can cause fire or explosion.
•All label and marking material must be cleaned with a damp cloth (or equivalent).
•The electronic monitoring system is required to be grounded. See Grounding instructions.
EQUIPMENT MISUSE HAZARD
Misuse can cause death or serious injury.
•Do not operate the unit when fatigued or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
•Do not exceed the maximum working pressure or temperature rating of the lowest rated system component. See Technical Specifications in all equipment manuals.
•Use fluids and solvents that are compatible with equipment wetted parts. See Technical Specifications in all equipment manuals. Read fluid and solvent manufacturer’s warnings. For complete information about your material, request MSDS from distributor or retailer.
•Do not leave the work area while equipment is energized or under pressure. Turn off all equipment and follow the Pressure Relief Procedure in this manual when equipment is not in use.
•Check equipment daily. Repair or replace worn or damaged parts immediately with genuine manufacturer’s replacement parts only.
•Do not alter or modify equipment.
•Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Call your distributor for information.
•Route hoses and cables away from traffic areas, sharp edges, moving parts, and hot surfaces.
•Do not kink or over bend hoses or use hoses to pull equipment.
•Keep children and animals away from work area.
•Comply with all applicable safety regulations.
PRESSURIZED EQUIPMENT HAZARD
Fluid from the gun/dispense valve, leaks, or ruptured components can splash in the eyes or on skin and cause serious injury.
•Follow Pressure Relief Procedure in this manual, when you stop spraying and before cleaning, checking, or servicing equipment.
•Tighten all fluid connections before operating the equipment.
•Check hoses, tubes, and couplings daily. Replace worn or damaged parts immediately.
THERMAL EXPANSION HAZARD
Fluids subjected to heat in confined spaces, including hoses, can create a rapid rise in pressure due to the thermal expansion. Over-pressurization can result in equipment rupture and serious injury.
•Open a valve to relieve the fluid expansion during heating.
•Replace hoses proactively at regular intervals based on your operating conditions.
PRESSURIZED ALUMINUM PARTS HAZARD
Use of fluids that are incompatible with aluminum in pressurized equipment can cause serious chemical reaction and equipment rupture. Failure to follow this warning can result in death, serious injury, or property damage.
•Do not use 1,1,1-trichloroethane, methylene chloride, other halogenated hydrocarbon solvents or fluids containing such solvents.
•Many other fluids may contain chemicals that can react with aluminum. Contact your material
supplier for compatibility.
PLASTIC PARTS CLEANING SOLVENT HAZARD
Use only compatible water-based solvents to clean plastic structural or pressure-containing parts. Many solvents can degrade plastic parts and cause them to fail, which could cause serious injury or property damage. See Technical Specifications in this and all other equipment instruction manuals. Read fluid and solvent manufacturer’s warnings.
TOXIC FLUID OR FUMES HAZARD
Toxic fluids or fumes can cause serious injury or death if splashed in the eyes or on skin, inhaled, or swallowed.
•Read MSDS’s to know the specific hazards of the fluids you are using.
•Route exhaust away from work area. If diaphragm ruptures, fluid may be exhausted with air.
•Store hazardous fluid in approved containers, and dispose of it according to applicable guidelines.
BURN HAZARD
Equipment surfaces and fluid that’s heated can become very hot during operation. To avoid severe burns:
•Do not touch hot fluid or equipment.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
You must wear appropriate protective equipment when operating, servicing, or when in the operating area of the equipment to help protect you from serious injury, including eye injury, inhalation of toxic fumes, burns, and hearing loss. This equipment includes but is not limited to:
•Clothing and respirator as recommended by the fluid and solvent manufacturer
•Protective eyewear, gloves, and hearing protection
Installation
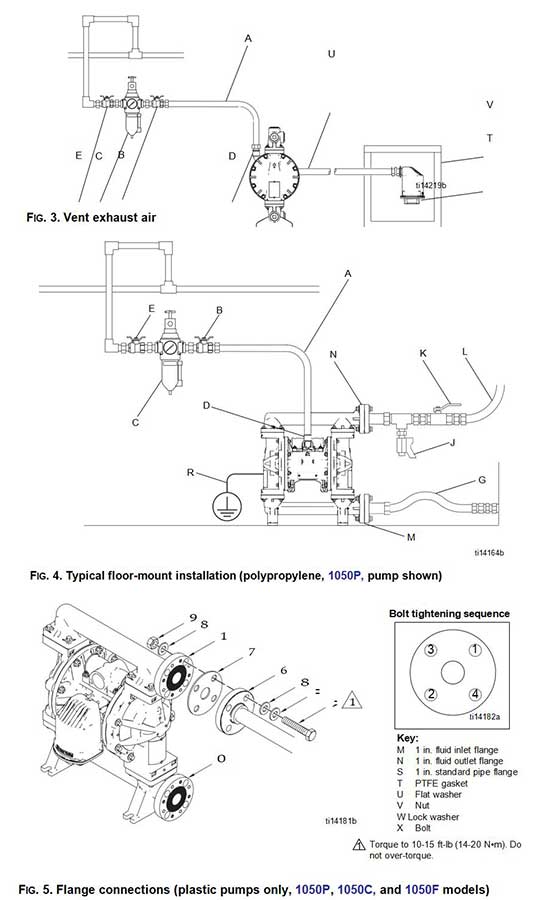
The Typical Installation shown in FIG. 4 is only a guide for selecting and installing system components. Contact your Graco distributor for assistance in planning a system to suit your needs.
Tighten Fasteners Before Setup
Before using the pump for the first time, check and retorque all external fasteners. Follow Torque Instructions, page 18.
Tips to Reduce Cavitation
Cavitation in a diaphragm pump is the formation and collapse of bubbles in the pumped liquid. Frequent or excessive cavitation can cause serious damage, including pitting and early wear of fluid chambers, balls, and seats. It may result in reduced efficiency of the pump. Cavitation damage and reduced efficiency both result in increased operating costs.
Cavitation depends on the vapor pressure of the pumped liquid, the system suction pressure, and the velocity pressure. It can be reduced by changing any of these factors.
1.Reduce vapor pressure: Decrease the temperature of the pumped liquid.
2.Increase suction pressure:
a.Lower the installed position of the pump relative to the liquid level in the supply.
b.Reduce the friction length of the suction piping. Remember that fittings add friction length to the piping. Reduce the number of fittings to reduce the friction length.
c.Increase the size of the suction piping.
NOTE: Be sure the inlet fluid pressure does not exceed 25% of the outlet working pressure.
3.Reduce liquid velocity: Slow the cyclic rate of the pump.
Pumped liquid viscosity is also very important but normally is controlled by factors that are process dependent and cannot be changed to reduce cavitation. Viscous liquids are more difficult to pump and more prone to cavitation.
Graco recommends taking all of the above factors into account in system design. To maintain pump efficiency, supply only enough power to the pump to achieve the required flow.
Graco distributors can supply site specific suggestions to improve pump performance and reduce operating costs.
Mounting
1.For wall mounting, order Graco Kit 24C637.
2.Be sure the mounting surface can support the weight of the pump, hoses, and accessories, as well as the stress caused during operation.
3.For all mountings, be sure the pump is bolted directly to the mounting surface.
4.For ease of operation and service, mount the pump so air valve, air inlet, fluid inlet and fluid outlet ports are easily accessible.
5.Rubber Foot Mounting Kit 236452 is available to reduce noise and vibration during operation.
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation will degrade natural polypropylene components of the pumps. To prevent potential injury or equipment damage, do not expose pump or the plastic components to direct sunlight for prolonged periods.
Grounding
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The equipment must be grounded to reduce the risk of static sparking. Static sparking can cause fumes to ignite or explode. Grounding provides an escape wire for the electric current. |
||||||
Pump: See FIG. 1. Loosen the grounding screw (GS). Insert one end of a 12 ga. minimum ground wire (R) behind the grounding screw and tighten the screw securely. Do not exceed 15 in-lb (1.7 N•m). Connect the clamp end of the ground wire to a true earth ground. A ground wire and clamp, Part 238909, is available from Graco.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polypropylene and PVDF: Only aluminum, conductive polypropylene, hastelloy, and stainless steel pumps have a ground screw. Standard polypropylene and PVDF pumps are not conductive. Never use a non-conductive polypropylene or PVDF pump with non-conductive flammable fluids. Follow your local fire codes. When pumping conductive flammable fluids, always ground the entire fluid system as described. |
||||||
Air and fluid hoses: Use only grounded hoses with a maximum of 500 ft (150 m) combined hose length to ensure grounding continuity.
Air compressor: Follow manufacturer’s recommendations.
Fluid supply container: Follow local code.
Solvent pails used when flushing: Follow local code. Use only conductive metal pails, placed on a grounded surface. Do not place the pail on a nonconductive surface, such as paper or cardboard, which interrupts grounding continuity.
Check your system electrical continuity after the initial installation, and then set up a regular schedule for checking continuity to be sure proper grounding is maintained.
Air Line
See FIG. 4, page 13.
1.Install an air regulator (C) and gauge to control the fluid pressure. The fluid stall pressure will be the same as the setting of the air regulator.
- Locate a bleed-type master air valve (B) close to the pump and use it to relieve trapped air. Be sure the valve is easily accessible from the pump and located downstream from the regulator.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trapped air can cause the pump to cycle unexpectedly, which could result in serious injury from splashing. |
||||||
3.Locate another master air valve (E) upstream from all air line accessories and use it to isolate them during cleaning and repair.
4.An air line filter (F) removes harmful dirt and moisture from the compressed air supply.
- Install a grounded, flexible air hose (A) between the accessories and the 1/2 npt(f) pump air inlet (D). Use a minimum 3/8 in. (10 mm) ID air hose.
Installation of Remote Pilot Air Lines
NOTICE
Pilot supply pressure should not exceed 25-50% of main air supply pressure. If pilot supply pressure is too high, the pump could leak air or exhaust excessive air at stall.
1.Connect an air supply line to the pump (A, FIG. 3, page 11).
2.Insert 5/32 OD tubing into the push-to-connect fitting on each pilot valve (113).
3.Connect remaining ends of tubes to external air signal, such as Graco’s CycleFlo™ (PN 195264) or CycleFlo II (PN 195265) controllers.
Reed Switch
Pulse Count models are intended for use with customer-supplied fluid management or inventory tracking systems. Attach an M12, 5-pin female cable to connect the reed switch to your data monitoring system. See Manual 406824.
Air Exhaust Ventilation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The air exhaust port is 3/4 npt(f). Do not restrict the air exhaust port. Excessive exhaust restriction can cause erratic pump operation.
To provide a remote exhaust:
- Remove the muffler (T) from the pump air exhaust port.
2.Install a grounded air exhaust hose (U) and connect the muffler (T) to the other end of the hose. The minimum size for the air exhaust hose is 3/4 in. (19 mm) ID. If a hose longer than 15 ft (4.57 m) is required, use a larger diameter hose. Avoid sharp bends or kinks in the hose.
3.Place a container at the end of the air exhaust line to catch fluid in case a diaphragm ruptures. If the diaphragm ruptures, the fluid being pumped will exhaust with the air.
Key:
A Air supply line
B Bleed-type master air valve
C Air filter/regulator assembly
D Air inlet
E Master air valve (for accessories)
T Muffler
U Grounded air exhaust hose
V Container for remote air exhaust
Fluid Supply Line
See FIG. 4, page 13.
1.Use grounded, flexible fluid supply lines (G). See
Grounding, page 9.
2.If the inlet fluid pressure to the pump is more than 25% of the outlet working pressure, the ball check valves will not close fast enough, resulting in inefficient pump operation. Excessive inlet fluid pressure also will shorten diaphragm life. Approximately 3 - 5 psi (0.02- 0.03 MPa, 0.21-0.34 bar) should be adequate for most materials.
3.For maximum suction lift (wet and dry), see Technical Specifications, page 24. For best results, always install the pump as close as possible to the material source.
Fluid Outlet Line
See FIG. 4, page13.
1.Use grounded, flexible fluid hoses (L). See
Grounding, page 9.
2.Install a fluid drain valve (J) near the fluid outlet.
3.Install a shutoff valve (K) in the fluid outlet line.
Key for FIG. 4:
A Air supply line
B Bleed-type master air valve (required for pump)
C Air filter/regulator assembly
D Air inlet
E Master air valve (for accessories)
G Grounded, flexible fluid supply line
J Fluid drain valve (required)
K Fluid shutoff valve
L Grounded, flexible fluid outlet line
M Fluid inlet (Aluminum, not pictured, four ports; Plastic, FIG. 4, center or end flanges available; Hastelloy and stainless steel, not pictured, one port)
N Fluid outlet (Aluminum, not pictured, four ports; Plastic, FIG. 4, center or end flanges available; Hastelloy and stainless steel, not pictured, one port)
R Ground wire (required for aluminum, conductive polypropylene, hastelloy, and stainless steel pumps;
Fluid Inlet and Outlet Ports
NOTE: Remove and reverse the manifold(s) to change the orientation of inlet or outlet port(s). Follow Torque Instructions on page 18.
Aluminum (1050A)
The fluid inlet and outlet manifolds each have four 1 in. npt(f) or bspt threaded ports. Close off the unused ports, using the supplied plugs.
Plastic (1050P, 1050C, 1050F)
The fluid inlet and outlet manifolds each have a 1 in. raised face ANSI/DIN flange (FIG. 4, M, N) in either a center or end location. Connect 1 in. standard flanged plastic pipe to the pump. See FIG. 5.
Graco standard pipe flange kits are available in polypropylene (239005), stainless steel (239008), and PVDF (239009). These kits include:
•the pipe flange
•a PTFE gasket
•four 1/2 in. bolts, spring lock washers, flat washers and nuts.
Be sure to lubricate the threads of the bolts and torque to 10-15 ft-lb (14-20 N•m). Follow the bolt tightening sequence and do not over-torque.



